316 Stainless Steel Solutions
316 Stainless Steel for Manufacturers In China
316 Stainless Steel (UNS S31600) is a premium austenitic stainless steel alloy known for its excellent combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. Enriched with molybdenum, it offers superior protection against chloride-induced corrosion, making it a preferred choice for harsh environments.
Advantages: 316 Stainless Steel provides exceptional corrosion resistance, outstanding durability in high-temperature conditions, and excellent machinability and weldability, allowing for versatile fabrication in industrial and marine applications.
Disadvantages: Compared to 304 stainless steel, 316 comes at a higher cost and its mechanical strength is slightly lower than certain martensitic stainless steels.
Comparison with Other Grades: While 304 is suitable for general-purpose applications, 316 outperforms it in marine, chemical, and food processing environments due to its enhanced corrosion resistance. Compared to 316L, standard 316 offers slightly higher strength but a similar resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for equipment exposed to aggressive conditions.
316 Stainless Steel By Shapes
Applications of 316 Stainless Steel
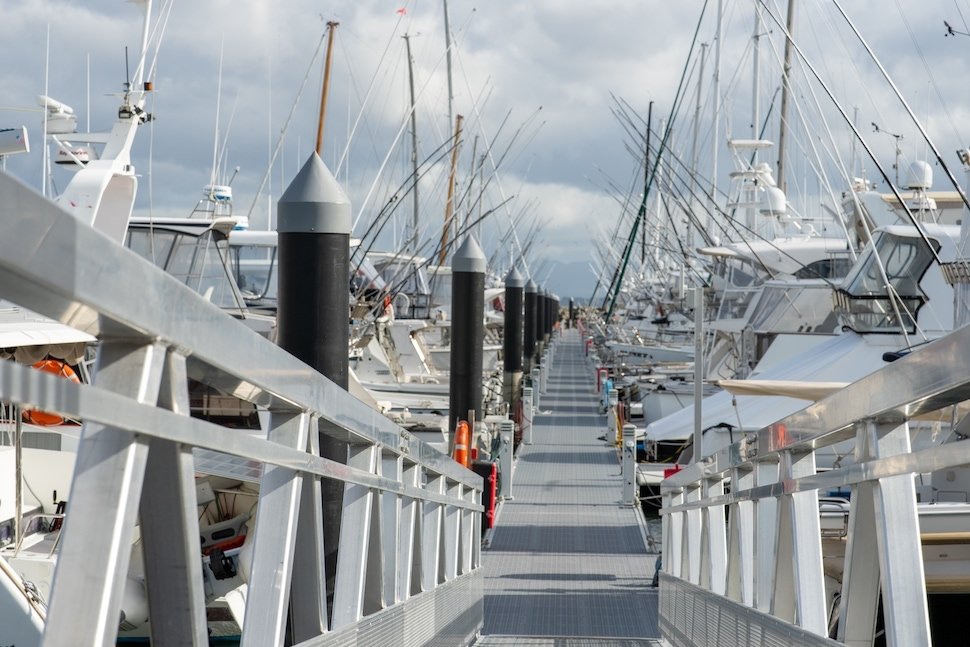
Industrial & Marine Applications: Ideal for chemical tanks, pumps, valves, seawater piping, and ship components, ensuring durability in harsh environments.
Food Processing, Pharmaceutical, and Chemical Equipment: Used in dairy equipment, pharmaceutical reactors, chemical storage tanks, and processing machinery, meeting strict hygiene standards.
Architectural & Engineering Uses: Suitable for outdoor cladding, bridge railings, rooftops, handrails, and decorative structures, offering corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.

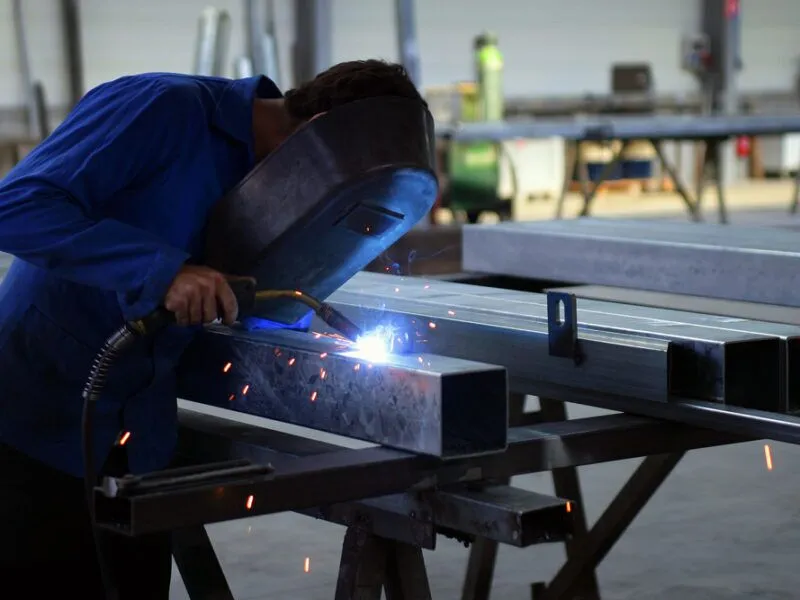
Machining, Welding, and Fabrication of 316 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel (UNS S31600) provides excellent versatility for machining, welding, and fabrication, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial and marine applications.
Machinability:
While 316 Stainless Steel is tougher to machine than 304 due to its work-hardening properties, it can be efficiently processed using specialized cutting tools and appropriate cutting fluids. Precision machining ensures accurate dimensions for custom components and assemblies.
Welding Guidelines:
316 Stainless Steel is compatible with TIG and MIG welding techniques. Proper control of the heat-affected zone is crucial to prevent carbide precipitation and maintain corrosion resistance. Post-weld annealing may be recommended for critical applications in aggressive environments.
Cutting, Bending, and Forming:
- Cold Bending: Maintain recommended bend radii to avoid cracking.
- Hot Working: Perform within controlled temperature ranges to preserve mechanical properties.
- Annealing: Restores ductility and reduces residual stresses after fabrication.
By following best practices in 316 stainless steel welding, machining and fabrication, manufacturers and suppliers can produce durable, corrosion-resistant, and precision-engineered components suitable for chemical, marine, food processing, and industrial equipment applications.

Chemical and Physical Properties of 316 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel (UNS S31600) combines a well-balanced chemical composition with superior mechanical and physical properties, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Its thermal properties further enhance performance in high-temperature environments, ensuring long-term reliability.
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Typical Content (%) | Function / Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.08 max | Improves strength but kept low to reduce carbide precipitation |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16–18 | Provides corrosion resistance and hardness |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10–14 | Enhances ductility and corrosion resistance |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2–3 | Increases resistance to chloride corrosion and pitting |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤2 | Improves hot working and strength |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤1 | Enhances oxidation resistance |
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 580–750 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 205–275 MPa |
| Elongation | 40–60% |
| Hardness | 79–97 HRB |
Physical Properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.0 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1375–1400°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 16.3 W/m·K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 16.0 µm/m·°C |
Thermal Properties & Heat Resistance:
Continuous service temperature: up to 870°C (short-term exposure up to 925°C)
Excellent thermal stability ensures minimal deformation in high-temperature industrial processes
High thermal conductivity and controlled expansion make it suitable for precision equipment and marine applications
These mechanical properties of 316 stainless steel and thermal properties contribute to its widespread use in chemical, marine, and food processing industries, providing both reliability and durability in harsh conditions.
Related Product

Brushed Stainless Steel

Etched Stainless Steel

Perforated Stainless Steel

Colored Stainless Steel